The world's largest iceberg "A23A" is on the verge of destruction!
The largest and oldest iceberg in the world is currently "A23A" (iceberg). Which broke off from the Filchner Ice Shelf in Antarctica in 1986. According to Wikipedia, the area of "A23A" iceberg may be about 3,500 square kilometers. Which is much larger than the small European country of Luxembourg or equal to Rhode Island. Where Luxembourg's area is 2,586 square kilometers.
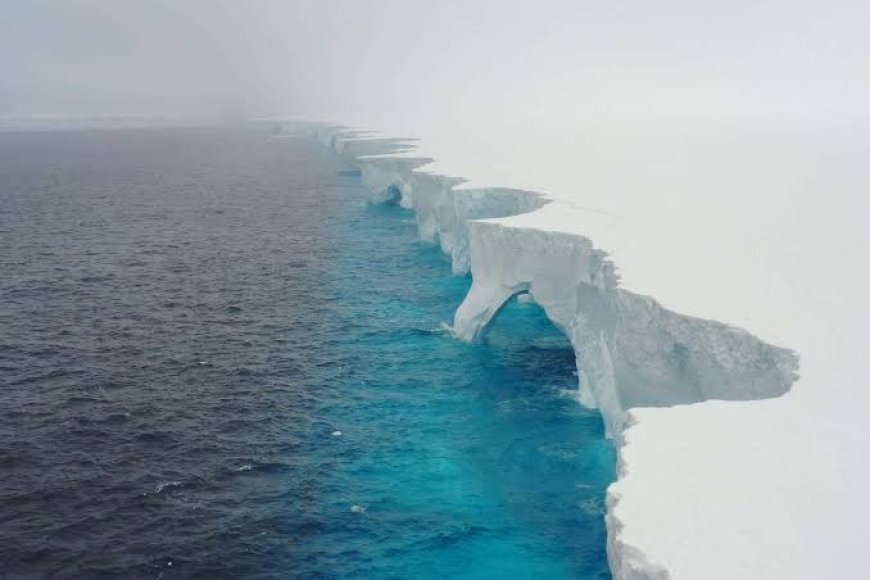

According to the BBC, the "A23A" iceberg once covered 3,900 square kilometers (1,500 square miles). It is now showing signs of extensive erosion and is gradually shrinking in size. The large amount of ice it contains is constantly melting, especially as it flows into warm oceans. The current estimated size of this iceberg is probably 3,234 square kilometers.
The "A23A" iceberg became stuck on a seafloor ridge after breaking away from Antarctica in 1986 and remained stuck there for about 37 years. However, in December 2023, it broke free from a marine cyclone (possibly an eddy) and began moving northward towards the Antarctic continent.
According to the BBC, this iceberg is now moving towards South Georgia Island. Which is considered a British Overseas Territory and a biodiversity hotspot. South Georgia Island is a mountainous barren island in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is located 1,300 kilometers east-southeast of the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas).
Environmental scientists expect that the "A23A" iceberg (iceberg) could completely break apart if it collides with South Georgia Island. This could bring about major changes to the natural environment of the region. In particular, such an accident could threaten the rich biodiversity that survives on South Georgia Island and its surrounding marine areas.
South Georgia currently has a special protected breeding area for penguins, seals and seabirds. If the iceberg gets stuck near the island, it could disrupt the food chain or collection route for animals. Since this iceberg is already floating, it is unlikely to increase sea level even if it melts. However, if it breaks into pieces, it could disrupt shipping at sea.
Currently, environmental scientists are closely monitoring the movement of the "A23A" iceberg with satellite images and other technical assistance. However, although the movement of the iceberg is completely natural, scientists believe that the detachment of ice in Antarctica is increasing at an alarming rate due to climate change and global warming.
Scientists have observed closely that this iceberg has most likely broken off as part of the natural growth cycle of the ice shelf. It is not due to the fossil fuel-driven climate crisis. However, according to them, global warming is bringing alarming changes to Antarctica. As a result, it may have devastating consequences for the rise in sea levels in the near future.
References: - BBC, CNN Climate, Wikipedia.